On Sunday morning (January 14, 2024), more than 100 flights got delayed, 10 flights were diverted, and some were even canceled at the Delhi airport as low visibility due to dense fog conditions hit flying operations.
Every winter, it’s the same story at Delhi and other major/minor airports around the country. Agitated passengers get stranded for hours and sometimes even a day waiting for the green ‘Now Boarding’ sign to turn up on the Flight Information Display Systems (FIDS).
However, today we’ll delve and talk about how despite these testing conditions and near-to-zero visibility, flights/aircrafts throughout the globe land and take off safely.
ILS: The technology that ensures safe flight landing
Fog, which is the suspension of water droplets near the ground, poses a considerable obstacle to aircraft operations during instances of reduced visibility. This atmospheric condition results in thick mist which hampers flight operations, necessitating the reliance on instruments like the “Instrument Landing System” (ILS) to navigate through the obscured surroundings.
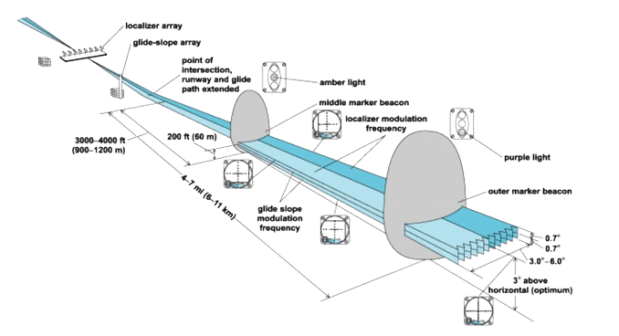
ILS is a standard International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) precision landing aid that is used to provide accurate azimuth (angular measurement in a spherical coordinate system) and descent guidance signals for guidance to flight for landing on the runway under adverse weather conditions.
To put things in perspective, ILS operates in tandem with ground-based equipment and avionic components on the aircraft, providing precise guidance to pilots during the critical phases of approach and landing. The ILS guiding system helps planes land in low visibility with the help of radio signals and also sometimes high-intensity lighting arrays. Among the various categories of ILS, Category 3 (CAT III) is the most significant due to its capability to support landing operations in low visibility conditions, thereby enhancing flight safety and operational efficiency.
At present, airports like Delhi, Amritsar, Jaipur, Lucknow, and Kolkata among others use CAT IIIB technology in India.
However, the absence of pilots or the ILS technology can lead to massive delays and cancellations. Moreover, a lot of financial and logistics are required to operate the technology which is still a distant dream at many airports around the country.
Demystifying ILS
Consisting of two main components—the localizer and the glide slope—the CAT safe system functions by transmitting radio signals that help pilots align their aircraft with the correct runway and maintain the appropriate descent path.
The localizer ensures lateral alignment, guiding the aircraft along the correct azimuth toward the runway centerline. Simultaneously, the glide slope provides vertical guidance, aiding pilots in maintaining the proper descent angle for a safe landing. Together, these components create a reliable and accurate navigational reference, allowing pilots to execute precision landings even when external visibility is severely compromised.
Notably, ILS-equipped runways are equipped with ground-based transmitters positioned at the end of the runway, emitting signals that are received by the aircraft’s onboard ILS receiver. As the aircraft approaches the runway, the pilot uses the visual and audible cues provided by the ILS to make real-time adjustments, ensuring that the aircraft remains aligned with the desired glide path.
In essence, the technology significantly enhances aviation safety and operational reliability by enabling pilots to conduct precise landings even in conditions that would otherwise pose a considerable risk.

