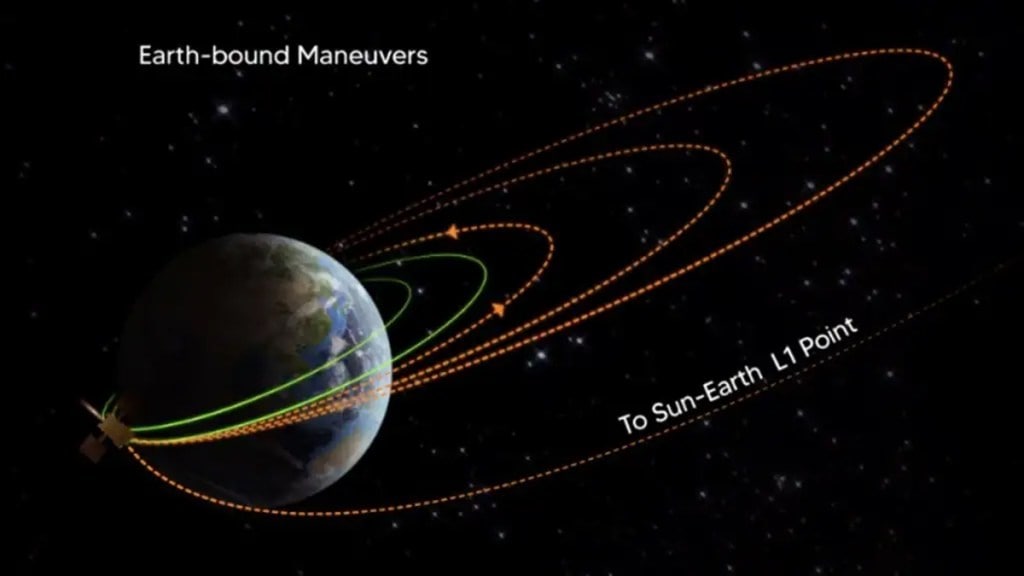
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has proudly announced the successful execution of the Trans-Lagrangean Point 1 Insertion (TL1I) manoeuvre during its maiden solar mission, Aditya-L1. This manoeuvre has positioned the spacecraft on a trajectory destined for the Sun-Earth L1 point.
ISRO’s Fifth Successful Celestial Transfer
In a remarkable feat, ISRO has achieved its fifth consecutive successful transfer of an object on a trajectory towards another celestial body or location in space. This achievement underscores ISRO’s consistent excellence in space exploration.
Launch and Mission Overview
The Aditya-L1 spacecraft embarked on its journey from the Satish Dhawan Space Station at Sriharikota in Andhra Pradesh. This historic mission holds several primary objectives, including scientific data collection and advancing India’s solar exploration endeavors.
Scientific Data Collection Commences
ISRO’s Aditya-L1 mission has commenced its scientific data collection phase. The STEPS instrument’s sensors have initiated measurements of supra-thermal and energetic ions and electrons at distances exceeding 50,000 km from Earth. This crucial data empowers scientists to analyze the behavior of particles surrounding our planet.
The Role of ASPEX Payload
The Supra Thermal and Energetic Particle Spectrometer (STEPS) instrument, a component of the Aditya Solar Wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX) payload, has also initiated its data-gathering operations. These data will contribute significantly to our understanding of the solar environment and its impact on Earth.