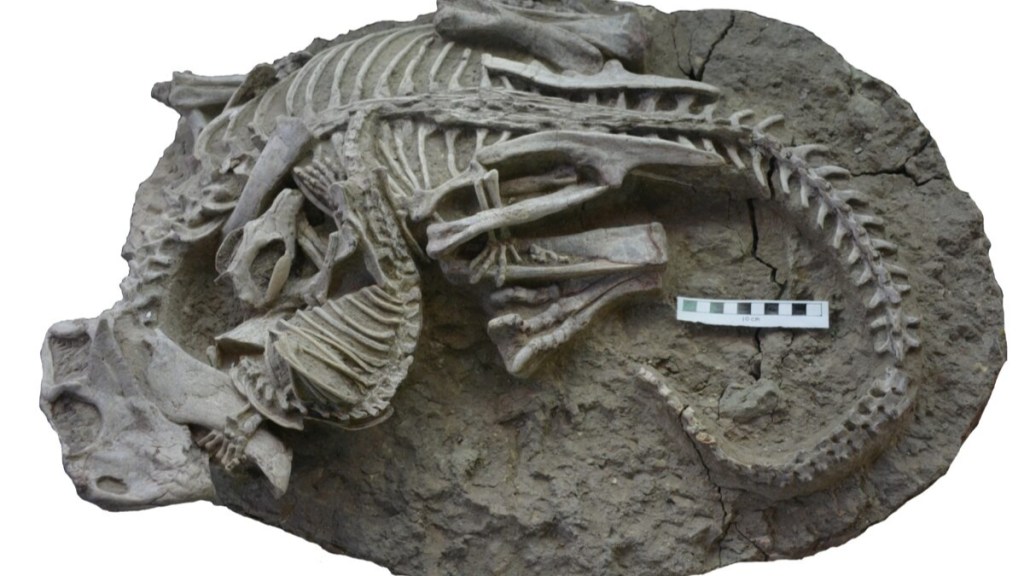
A 125 millions years old unusual fossil has been described by Canadian and Chinese scientists which shows the exact moment a carnivorous mammal attacked a plant-eating dinosaur.
Dr Jordan Mallon, a paleobiologist with the Canadian Museum of Nature and a co-author of the study, said the two animals are locked in a “mortal combat, intimately intertwined”. He added that it is one of the first pieces of evidence which show “actual predatory behaviour by a mammal on a dinosaur”.

Where was the fossil found?
The fossil was discovered in China’s Liaoning Province in 2012. Bothe skeletons in the fossil are nearly complete. This is due to the area where they were found. The Liujitun fossil beds have often been dubbed as “China’s Dinosaur Pompeii”. The name refers to the fossils of dinosaurs, small mammals and other animals that were buried by mudslides and debris following one or more volcanic eruptions.
About the fossil
The well-preserved fossil has a dinosaur which has been identified as a species of Psittacosaurus, which is about the size of a large dog. The dinosaur species is among the earliest known horned dinosaurs and lived around 125 to 105 million years ago in Asia during the Early Cretaceous period. The mammal on the other hand is a badger-like animal called Repenomamus robustus.
Before the discovery of this fossil, scientists knew Repenomamus preyed on dinosaurs as fossiled baby bones of Psittacosaurus were found in its stomach.
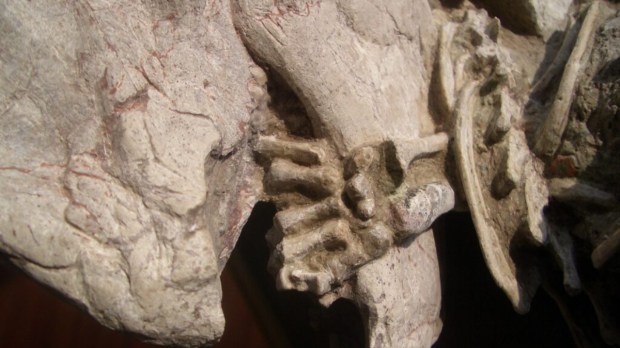
The examination of the fossil shows the dinosaur was lying prone, with its hindlimbs folded on either side of its body. The mammal is gripping the jaw of the larger dinosaur. It sits on top of its prey. It is also biting some of the ribs of the dinosaur and the back foot of the Repenomamus is gripping onto its hind leg, Dr Mallon said.

The scientists ruled out the possibility that the mammal was simply scavenging a dead dinosaur. They said it’s unlikely that the two animals would become so entangled had the dinosaur been dead. The mammal’s position also shows that it was the aggressor. The dinosaur’s bones have no tooth marks, suggesting it was not being scavenged.
This rare fossil is now in the collections of the Weihai Ziguang Shi Yan School Museum in China’s Shandong Province.


