JERA and Toyota announce the construction and launch of Sweep Energy Storage System. The system has been built using batteries reclaimed from electrified vehicles (HEV, PHEV, BEV, FCEV) and is connected to the consumer electrical power grid. It begins operation starting October 27.
In the future, demand for storage batteries is expected to grow as they become necessary supply-stabilising tools when expanding renewable energy in the movement toward CO2 emissions reduction, a vital part of achieving carbon neutrality.
At the same time, limited supplies of battery materials including cobalt and lithium, mean there is an ongoing need for environmentally conscious initiatives, such as reclaiming used electrified vehicle batteries for effective use as storage batteries.
In response, JERA and Toyota began discussions in 2018 to establish battery reuse technologies, which eventually led to this capacity, grid-connected Sweep Energy Storage System.
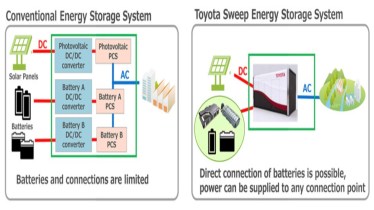
Toyota’s new storage system is equipped with a function called sweep, which allows the use of reclaimed vehicle batteries, which have significant differences in performance and capacity, to their full capacity regardless of their level of deterioration.
The sweep function, developed by Toyota Central R&D Labs is a device that can freely control energy discharge by switching electricity flow on and off (bypassing) through series-connected batteries in microseconds.
Furthermore, the sweep function also enables direct AC output from the batteries, while reusing onboard inverters eliminate the need for a power conditioner (PCS). That contributes to reducing costs and helps avoid power loss when converting from AC to DC by PCS, with the aim of improving effective energy use.
The project plans to operate grid storage batteries for recharge and discharge operations, connected to the Chubu Electric Power Grid power distribution system from a facility at JERA’s Yokkaichi Thermal Power Station.
JERA and Toyota aim to introduce approximately 100,000 kWh of supplied electricity in the mid-2020s, thereby not only reducing the overall cost of the energy storage system but also contributing to the reduction of CO2 emissions.
In addition, JERA is developing a low environmental impact process for recycling lithium-ion batteries for electrified vehicles which Toyota plans to support by leveraging the knowledge it has accumulated through its battery recycling initiatives to date.
By collecting used batteries and reusing resources, both companies hope to accelerate their efforts toward achieving a resource-recycling society.
JERA will continue to work not only within the energy industry but also with leading companies in Japan and overseas to develop technologies such as battery storage systems and services that contribute to optimal energy utilisation toward achieving a decarbonised and resource-recycling society.